Strokes - What You Need to Know
Stroke has been and is still a very common disease today. If you or your loved one has suffered a stroke, below is everything you need to know.
What Is a Stroke?
Stroke is a disease that occurs when blood stops flowing/reaching the brain i.e. due to a torn blood vessel or blood clot. A stroke can either be mild or severe. A stroke can also be temporary or permanent. A stroke usually affects a person’s speech, vision, behaviour as well as the ability to think and move certain parts of the body. The effects usually vary depending on factors such as the area of the brain that is affected, the extent of the damage as well as how fast normal blood flow can be restored in the affected area. In very severe cases, a stroke can cause death.
Types of Stroke
There are five main types of stroke namely;
- Ischemic Stroke
- Embolic Stroke
- Thrombosis Stroke
- Hemorrhagic Stroke
- TIA (Transient Ischemic Attack)
a. Ischemic Stroke
Ischemic stroke results from a clot or mass clogs in blood vessels which cut off blood flow to the brain.
b. Embolic Stroke
Embolic Stroke results from a blood clot which forms somewhere else in the body (in most cases the heart) and travels via the bloodstream to the brain. Once the blood clot reaches the brain, it travels to a small blood vessel blocking its passage.
c. Thrombotic Stroke
This type of stroke occurs when one of the arteries (or many arteries) responsible for supplying blood to the brain are blocked impairing blood flow. Thrombotic stroke derives its name from the fact that clots that form on blood vessels deposit what are known as a thrombus. The underlying cause of blood-clot strokes is unhealthy blood vessels i.e. blood vessels which are clogged by cholesterol and fatty deposits.
d. Hemorrhagic Stroke
As the name suggests, this type of stroke is caused by hemorrhage i.e. when one or many blood vessels rupture resulting in an accumulation of blood in the surrounding tissue. Hemorrhagic Stroke can be caused by injury, weakening of specific regions of blood vessels as well as the abnormal formation of blood vessels.
e. TIA (Transient Ischemic Attacks)
TIAs are small/mini strokes which are caused when a blood clot temporarily blocks an artery. As a result, TIA symptoms/effects are usually temporary.
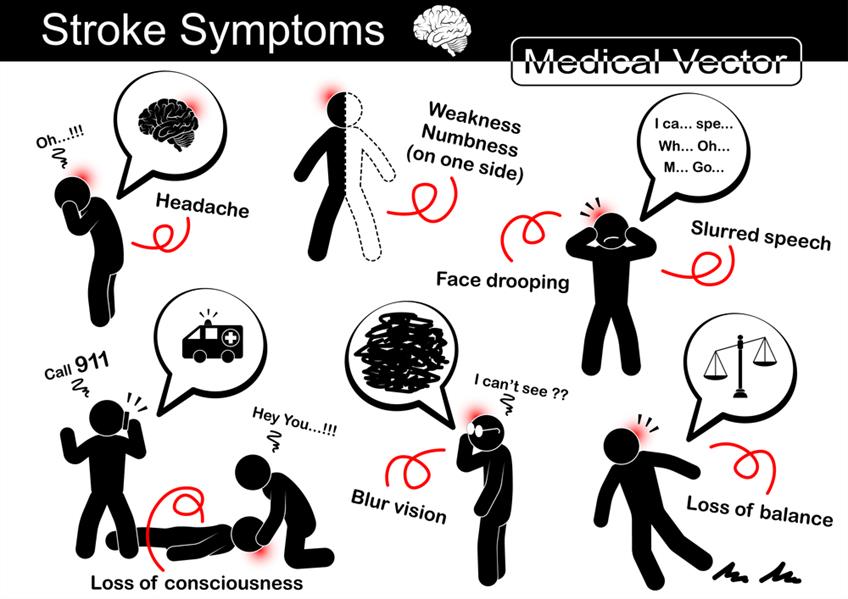
Symptoms of a Stroke
How Do You Know If You/Your Loved One Is Suffering from a Stroke?
The main stroke symptoms include;
- Facial Weakness (Especially on One Side)
- Arm Weakness
- Slurred Speech (In Severe Cases, a Person May Be Unable to Speak)
It’s also worth noting that there are many other symptoms to look out for i.e. visual problems, balance problems, falling and headaches. You should also be on the lookout for body function problems since a stroke affects the brain which is the organ responsible for controlling all body functions.
Important: If you or a loved one experiences any one or more of these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately. Seeking immediate medical care early is important because it lessens the effects of the stroke.
How Is a Stroke Diagnosed?
A Stroke is usually diagnosed via physical examination as well as diagnostic studies. A patient’s medical history also helps in diagnosis. Doctors usually perform an MRI or CT scan on patients suspected to have suffered a stroke. The scan helps doctors establish whether a patient has a clot anywhere or if they are suffering from internal bleeding.
Diagnosis may also involve ultrasound, magnetic resonance angiography (scan to evaluate blood flow), angiogram (artery x-ray) as well as other lab tests/x-rays if a patient is suspected to have a stroke caused by artery disease.
Treatment
As mentioned above, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention if you have any of the above stroke symptoms to increase your chances of recovery/reduce the severity of the effects of suffering a stroke.
If you suffer from a stroke caused by a blood clot/s, there is medication for dissolving blood clots. If you receive such medication in time, your chances of having a full recovery will be higher. Besides medication, treatment may also include surgery in severe cases.
Physical therapy is also a common and effective stroke treatment administered to individuals who develop muscle strength and balance problems after a stroke.
Speech therapy is also effective for helping stroke patients who have speech problems. Medical professionals like speech and language therapists (SLTs) can help stroke patients work on their speech as well as related activities i.e. drinking and eating which may be affected by a stroke.
In cases where a patient’s leg or arm in paralyzed, a medical professional like an occupational therapist can assist a patient to learn how to perform important tasks i.e. dress, bathe, cook, etc.
Related Posts

Speech requires the coordination of a range of muscles, including those controlling the larynx and the vocal cords, the lips, the tongue, the jaw and the respiratory system. The brain plans the movements and puts them into motion. Difficulties in this process may result in apraxia or dysarthria. Apraxia is a disorder where messages from the brain to the mouth are interrupted, making it difficult for someone to move his or her lips or tongue to the right place to say sounds correctly. It does not mean there is muscle weakness. A common cause of apraxia is a stroke . Other causes include Traumatic Brain Injury , such as from a motor vehicle accident, Dementia , brain tumours, and progressive neurological disorders, such as ALS. Speech is often slow, laboured and halting. Dysarthria results from the impaired movement of the muscles used for making speech sounds, including the lips, tongue, vocal folds, or diaphragm. It is caused by damage to the brain, which can happen at birth (cerebral palsy), or later in life due to injury, stroke or neurological illnesses. Symptoms of dysarthria can include slow or rapid speech, speech that is difficult to understand, and abnormal pitch, rhythm and voice quality.






